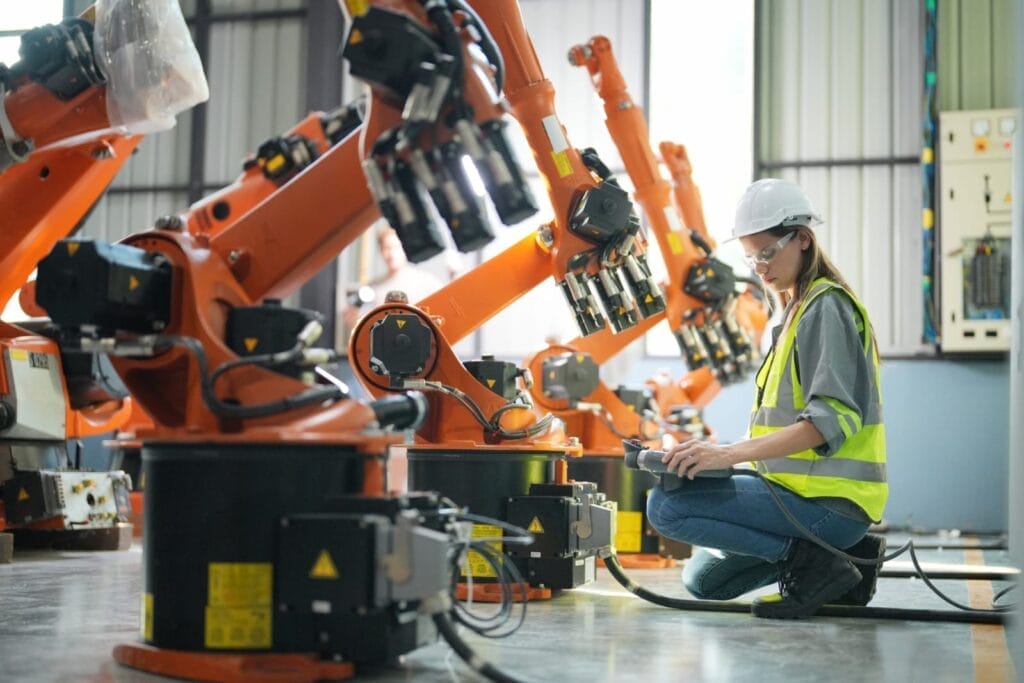
Manufacturing environments are often filled with potential hazards. Moving parts, sharp edges, and powerful machinery all pose significant risks to workers. Machine guarding serves as a critical defense against these dangers, creating vital barriers between employees and the equipment that could cause them harm. When implemented correctly, machine guarding solutions protect workers, improve operational efficiency, and support regulatory compliance. In today’s manufacturing landscape, effective machine guarding isn’t optional, it’s essential for creating a workplace where safety and productivity coexist.
Understanding Machine Guarding Fundamentals
Machine Guarding for Safer Manufacturing refers to safeguards designed to protect operators and other employees from hazards created by moving machine parts. These guards create a physical barrier that prevents contact with dangerous areas of the machinery. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) requires guards on all machines with hazardous moving parts.
Effective machine guarding serves multiple purposes. It prevents contact with dangerous components. It contains debris that might be ejected during operation. Guards also protect against other potential dangers like electrical hazards or excessive noise. The key is finding solutions that protect workers without impeding the manufacturing process itself.
Types of Machine Guards
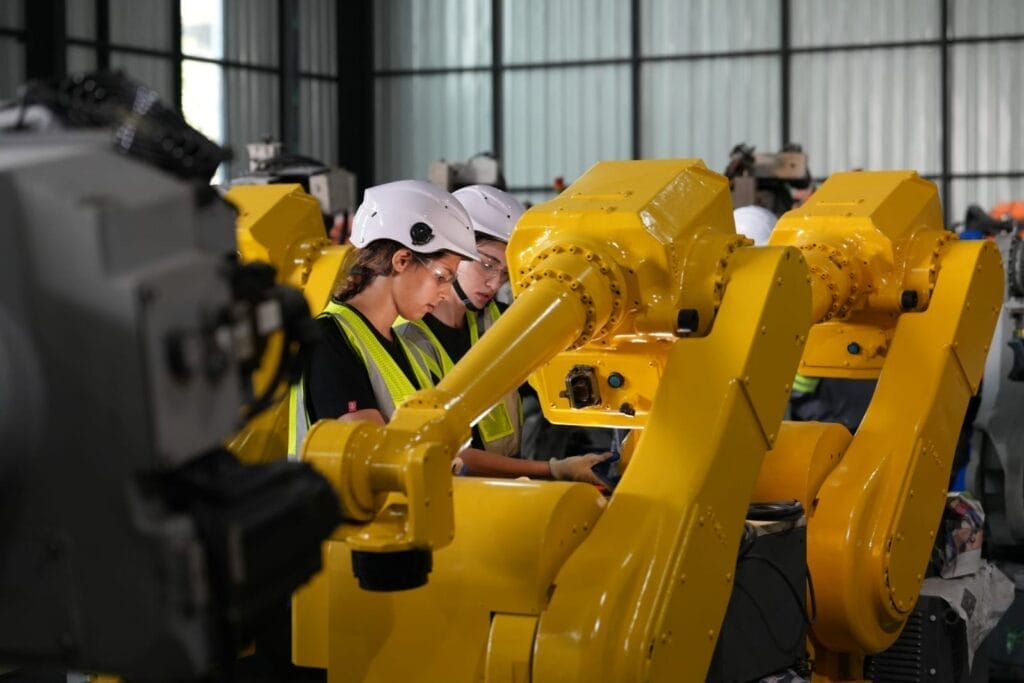

Different manufacturing environments require different guarding approaches. Here are the primary types:
- Fixed Guards – Permanent barriers that require tools to remove. These offer consistent protection from hazards that don’t require frequent access.
- Interlocked Guards – Guards connected to the machine’s power source and automatically shut down the equipment when the guard is removed or opened.
- Adjustable Guards – Can be adjusted to accommodate different sizes of processed materials while maintaining protection.
- Self-Adjusting Guards – Move into position based on the material being worked on, protecting while allowing material to pass through.
- Presence-Sensing Devices – Use light curtains, pressure mats, or similar technology to detect when a worker enters a danger zone and automatically stop the machine.
The best solution often involves a combination of these approaches. Modern manufacturing facilities typically implement a layered protection strategy.
Key Considerations for Effective Machine Guarding
When implementing machine guarding solutions, manufacturers must balance safety with practicality. Guards should prevent access to danger zones without creating new hazards or significantly impeding productivity. Visibility is crucial—operators must see the process clearly, even with guards in place.
Maintenance requirements deserve careful thought as well. Guards that are difficult to remove for necessary maintenance might be bypassed by frustrated workers, creating even greater hazards. Training plays an essential role too. Even the best guarding solutions require proper worker education about their purpose and proper use.
Material selection matters significantly. Guards must be constructed of materials strong enough to withstand impacts and prevent access to hazards. They should also be resistant to chemicals or conditions present in the specific manufacturing environment. Different processes may require guards made of steel, polycarbonate, mesh, or other materials based on specific protection needs.
Machine Guarding Regulations and Standards
OSHA requirements form the regulatory foundation for machine guarding in the United States. These regulations are detailed in 29 CFR 1910.212 and related standards. Compliance isn’t just about avoiding penalties—it’s about creating genuinely safer workplaces.
Beyond OSHA, industry-specific standards from organizations like the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) provide detailed guidance for particular types of machinery. International standards such as ISO 13857 address safety distances to prevent hazardous zones being reached. Manufacturers operating globally should be aware of varying requirements across different regions.
Regular inspections are necessary to ensure continued compliance. Guards can become damaged or be improperly reinstalled after maintenance. Implementing a formal inspection schedule helps identify and address these issues before they lead to accidents.
Technological Advances in Machine Guarding
Today’s manufacturing environments benefit from significant technological improvements in machine guarding. What was once limited to simple physical barriers has evolved into sophisticated, integrated safety systems that protect workers while optimizing production efficiency. These advances have transformed how industries approach workplace safety.
Smart Interlocking Systems
Modern interlocking systems have become remarkably sophisticated. Unlike basic mechanical interlocks, today’s systems incorporate electronic monitoring with redundant circuits to ensure fail-safe operation. These systems can detect when a guard is opened and if an interlock has been tampered with or bypassed. Some advanced interlocks even track access patterns, logging when and how often guards are opened, enabling management to identify potential process improvements or training needs.
Time-delayed interlocks represent another significant advancement. These systems prevent access until dangerous motion has completely stopped, protecting workers from machinery that continues to move after power is removed. The integration of these interlocks with machine control systems has become seamless, allowing for zone-specific shutdowns that maintain productivity in unaffected areas.
Advanced Presence Detection
Presence-sensing technology has undergone revolutionary improvements. Traditional light curtains have been enhanced with muting capabilities that allow materials to pass through while still detecting human intrusion. Area scanners using LIDAR technology can create configurable safety zones around dangerous equipment, distinguishing between people and authorized materials.
Vision systems now incorporate artificial intelligence to differentiate between workers and equipment, creating more intelligent safety responses. These systems can identify when someone is approaching a danger zone and trigger graduated responses—first warnings, then slowing operations, and finally complete stops if the person continues to approach. This nuanced approach maintains productivity while ensuring safety.
Radio frequency identification (RFID) technology has also entered the machine guarding space. Personal safety transponders can be integrated into employee badges, allowing machines to detect exactly who is present and adjust safety parameters based on training level and authorization.
Implementation Best Practices
Successful implementation begins with a thorough risk assessment. Identifying all potential hazards allows manufacturers to develop comprehensive guarding strategies tailored to specific needs. Involving operators and maintenance personnel in the planning process improves both the practicality and acceptance of guarding solutions.
Training represents a critical component. Workers need to understand not just how guards’ function but why they matter. Creating a safety culture where bypassing guards is considered unacceptable helps ensure consistent protection.
Documentation provides the foundation for ongoing compliance. Detailed records of risk assessments, guard specifications, inspection schedules, and training programs demonstrate due diligence and support continuous improvement efforts.
Effective machine guarding solutions are essential components of any comprehensive manufacturing safety program. When properly selected and implemented, they protect workers from serious injuries while supporting productive operations. The landscape of machine guarding continues to evolve with technological advances offering increasingly sophisticated protection options. By understanding the fundamentals, staying current with regulations, embracing appropriate technologies, and following implementation best practices, manufacturers can create safer environments for everyone in their facilities.