In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, app development companies play a pivotal role in shaping the way we interact with technology. The success of an app often hinges on how well it meets the needs and expectations of its users. To achieve this, developers must continuously evolve and adapt their apps to provide the best user experience possible. This process is made possible through a methodology known as iterative design, which involves collecting and acting upon user feedback to refine and enhance the app.
App development companies, whether they are startups or established giants, are always in pursuit of delivering a top-notch user experience. This requires a deep understanding of the target audience, their needs, and their pain points. Creating an app that addresses these factors effectively is a challenge, but it is a challenge that iterative design approaches head-on.
The Iterative Design Process: A Brief Overview
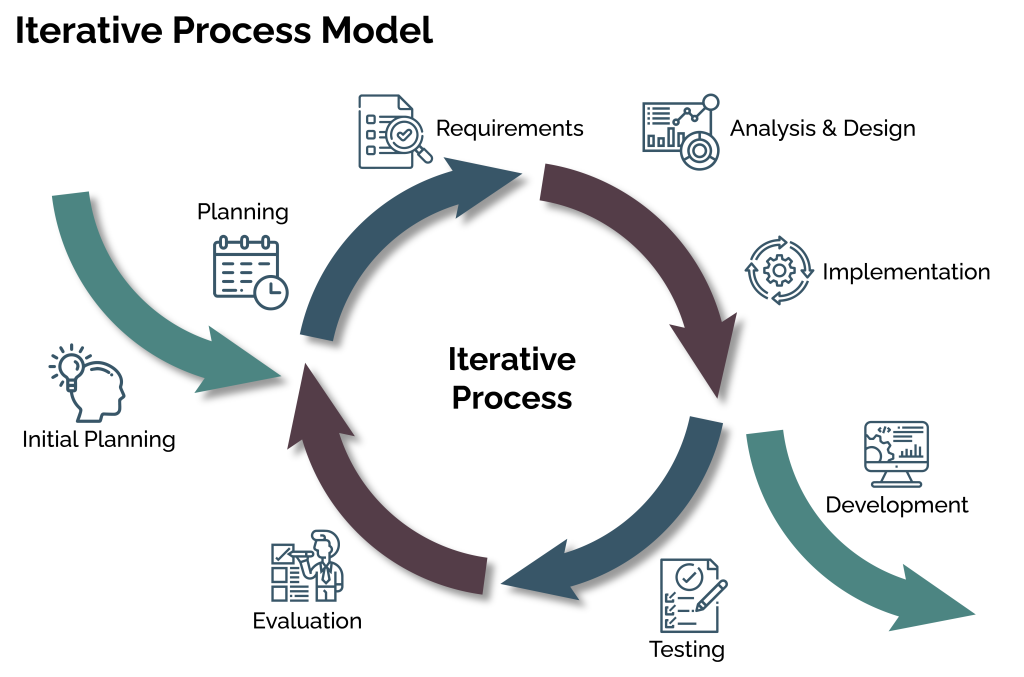
Iterative design is a methodology that emphasizes incremental improvements in the development of an app. It involves a cyclical process of design, implementation, testing, and refinement, with user feedback serving as a critical input throughout. The iterative design process typically follows these key steps:
1. Initial Design: App development companies start with a preliminary design of the app, taking into consideration the intended functionality and user interface. This design often serves as the foundation on which the app is built.
2. Prototype Development: Developers create a prototype or a minimum viable product (MVP) based on the initial design. This MVP is a functional but basic version of the app that can be used for testing.
3. User Testing: The MVP is made available to a select group of users or beta testers. Their feedback and insights are crucial in understanding how the app is performing and what improvements are needed.
4. Feedback Analysis: App development companies meticulously analyze the feedback received from users. This includes identifying pain points, feature requests, and any bugs or usability issues.
5. Iteration: Based on the feedback, developers make necessary improvements and enhancements to the app. This often involves changes to the user interface, bug fixes, and feature additions or modifications.
6. Repeat: The cycle repeats, with the improved version of the app being tested and refined again. This process continues until the app reaches a point where it meets the desired quality and user experience standards.
The Role of User Feedback in Iterative Design
User feedback is at the heart of the iterative design process. It provides a vital perspective on how the app is performing in the real world. Here are some key aspects of how user feedback shapes app development:
1. Bugs and Usability Issues: User feedback helps in identifying and resolving bugs and usability issues. Users often report issues that developers might not have encountered during internal testing. This leads to a more polished and reliable app.
2. Feature Prioritization: Users’ preferences and needs can change over time. Through feedback, app development companies can prioritize features and functionalities that matter most to their users. This ensures that the app remains relevant and competitive.
3. Enhanced User Experience: User feedback provides insights into the user experience. This includes not just technical issues but also the overall look and feel of the app. Developers can adjust the interface and design to enhance user satisfaction.
4. Adapting to Market Trends: The digital landscape is dynamic, and market trends can shift quickly. User feedback can help an app development company to stay agile and adapt to these trends by making timely adjustments to the app’s features and capabilities.
5. User Retention and Growth: Addressing user feedback positively impacts user retention and can lead to organic growth through word-of-mouth recommendations. Satisfied users are more likely to continue using the app and recommend it to others.
Examples of App Development Companies Using Iterative Design
Many successful app development companies have harnessed the power of iterative design to create and maintain their apps. Let’s look at a couple of notable examples.
1. Facebook: Facebook, one of the world’s leading social media platforms, has a long history of iterative design. They constantly gather user feedback and roll out updates to improve their app’s performance and user experience. Features like the News Feed, Timeline, and Stories have all evolved based on user input.
2. Spotify: Spotify, a popular music streaming service, regularly updates its app based on user feedback. They have introduced features like playlists, personalized recommendations, and collaborative playlists to enhance the user experience, all driven by feedback from millions of users.
3. Instagram: Instagram, a subsidiary of Facebook, is another prime example. This photo-sharing app continually evolves its interface and features to keep up with user expectations. Features like Stories, IGTV, and shopping integration have been introduced following user feedback.
These companies understand that iterative design is not a one-time process but an ongoing commitment to enhancing the user experience. They leverage feedback to remain competitive in a rapidly changing industry.
Challenges in Implementing Iterative Design
While iterative design is a powerful approach, it comes with its own set of challenges, especially for app development companies. Some of these challenges include:
1. Resource Allocation: Continuously refining an app based on user feedback can be resource-intensive. It requires a dedicated team and financial investments to ensure that the iterative process is sustainable.
2. Balancing Feedback: An app development company must prioritize and filter user feedback. Not all suggestions and criticisms are equally valuable, and discerning which ones to act on can be challenging.
3. Technical Debt: Frequent iterations can lead to what’s known as “technical debt,” where quick fixes and short-term solutions accumulate, making the app’s codebase more complex and difficult to maintain.
4. User Expectations: Users may have unrealistic or contradictory expectations, making it challenging to meet everyone’s demands. Striking a balance between user feedback and the app’s overall vision can be tricky.
5. Competitive Pressure: App development is highly competitive, and the pressure to release new features and updates quickly can lead to rushed decisions that may not align with the iterative design process.
Conclusion
App development companies are at the forefront of technological innovation, and the success of their apps hinges on their ability to provide a stellar user experience. The iterative design approach is a powerful tool that allows these companies to continuously adapt and evolve their apps based on user feedback.
Through a cyclical process of design, testing, feedback analysis, and refinement, app development companies can create apps that meet user expectations and stay competitive in the dynamic digital landscape. User feedback serves as the compass guiding their development journey, ensuring that the app remains relevant and user-centric.
While iterative design is not without its challenges, the benefits far outweigh the drawbacks. It allows app development companies to create products that users love, driving user retention, growth, and long-term success. In a world where app users have countless choices at their fingertips, the ability to adapt to user feedback is a defining characteristic of the most successful app developers.